A digital twin is a virtual replica of a real-world object, system, or process powered by real-time data, IoT sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI). It continuously simulates, predicts, and optimises performance, allowing businesses to test scenarios without touching the physical asset.
By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, digital twins empower industries to make smarter decisions, boost operational efficiency, and drive innovation at scale.
To explore how global leaders like IBM are transforming industries through digital twin technology, learn more here.
- Introduction
- What Is Digital Twin Technology?
- How Does Digital Twin Technology Work?
- Core Components of a Digital Twin
- Benefits of Digital Twin Technology
- Real-World Applications & Case Studies
- Challenges and Considerations
- How to Implement Digital Twin Technology: Step-by-Step Guide
- Future Trends: 2025–2030
- Conclusion
- FAQ's
Introduction
Imagine you could test changes to a jet engine, factory line, or city traffic system before actually touching the real thing, and see exactly how it would respond in real life. That is what digital twin technology allows.
Once a futuristic concept, digital twins are now a core part of industries like manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and smart cities, thanks to advancements in IoT sensors, AI, and cloud computing.
According to Markets, the global digital twin market is projected to grow from $10.1 billion in 2023 to over $110 billion by 2030, making it one of the fastest-growing tech trends today.
What Is Digital Twin Technology?
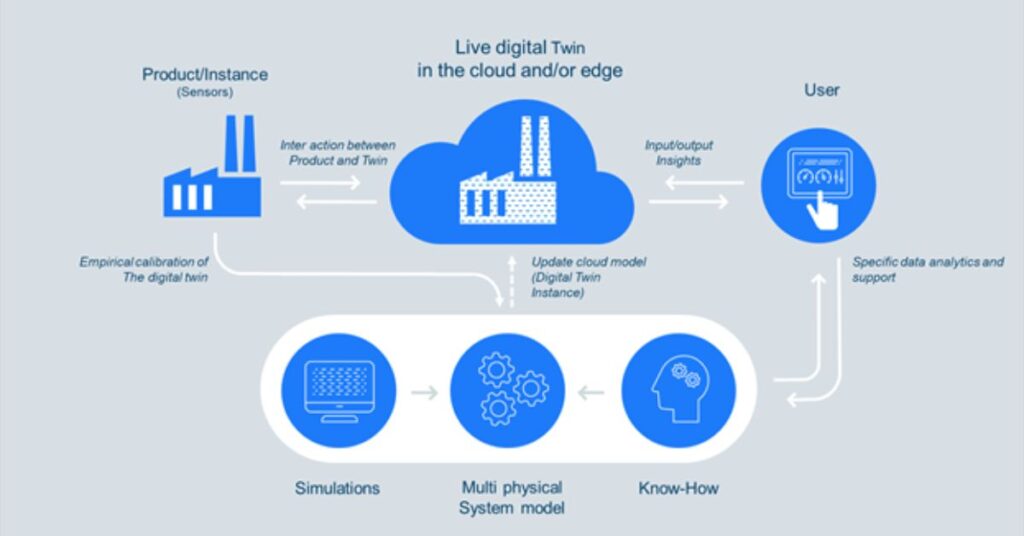
A digital twin is more than just a 3D model. It is a living, data-driven simulation that mirrors a physical object or system in real time.
Think of it like a “SimCity” game, but for real-world systems. You can monitor performance, run “what-if” scenarios, and predict future issues, all without risking damage to the actual asset.
Key capabilities include:
- Real-time monitoring via IoT sensors
Enables continuous tracking of equipment performance, allowing instant detection of anomalies and downtime risks through real-time data analytics. - Predictive analytics to forecast failures
Uses machine learning algorithms and historical data to identify early signs of wear or malfunction, helping industries reduce maintenance costs. - Optimisation tools to improve efficiency
Employs AI-driven insights and digital simulations to fine-tune operations, enhance productivity, and minimise energy consumption. - Simulation for testing design or process changes
Allows businesses to safely test new product designs or workflow adjustments in a virtual environment before applying them to real-world systems.
How Does Digital Twin Technology Work?
Here is the step-by-step process behind how digital twins function:
- Data Collection: Physical assets are equipped with IoT sensors to gather data on temperature, pressure, vibration, speed, and more.
- Data Integration: Information flows into a cloud platform where it is cleaned, processed, and stored.
- Model Creation: Engineers create a 3D or mathematical model of the asset using CAD tools or simulation software.
- AI & Analytics: Machine learning algorithms analyse patterns and predict outcomes.
- Visualisation & Testing: Users can see how the asset behaves under different scenarios and make adjustments.
While digital twins offer tremendous value, they also introduce data security and privacy challenges. Businesses should prioritise enhancing cybersecurity measures for digital twin systems to protect sensitive data and maintain trust in connected environments.
Core Components of a Digital Twin
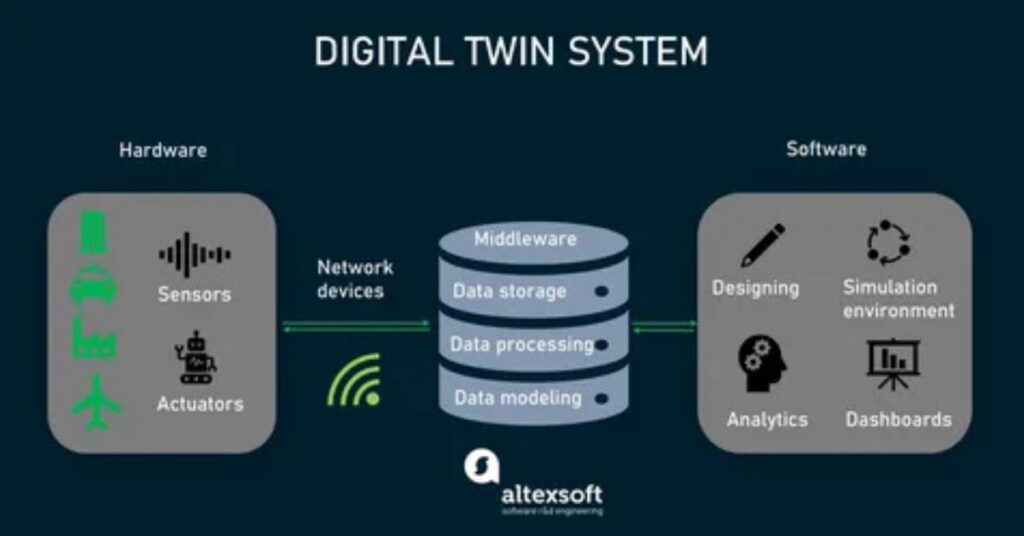
To function effectively, digital twins rely on several technological pillars:
- IoT Devices
Smart IoT sensors continuously track data such as temperature, vibration, and pressure from physical assets, ensuring real-time monitoring and accurate feedback. (Learn about IoT from Cisco). - Cloud Computing
Offers scalable data storage, fast processing, and seamless connectivity between systems, allowing companies to access and analyse data from anywhere in the world. - Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Drives intelligent predictions, automated insights, and process optimisation by analysing complex data patterns and simulating outcomes for better decision-making. - Simulation Software
Provides 3D visualisation and virtual testing environments that help engineers understand performance under different scenarios before making real-world changes. - Data Integration Tools
Merge information from multiple systems, such as IoT platforms, ERP software, and analytics dashboards, to create a unified digital ecosystem for efficient data-driven decision-making.
Benefits of Digital Twin Technology
Here are key advantages that make digital twins game-changers across industries:
- Predictive Maintenance
Fix issues before they happen, reducing costly downtime and preventing unexpected equipment failures. With AI-driven analytics and real-time monitoring, digital twins help industries schedule maintenance proactively and extend the lifespan of critical assets. - Cost Savings
Avoid expensive trial-and-error in physical systems by running virtual simulations instead. Businesses can test multiple design or process scenarios digitally, minimising material waste and saving both time and operational costs. - Faster Innovation
Test and refine new ideas virtually before implementing them in the real world. This accelerates product development cycles, reduces risks, and allows companies to bring innovative solutions to market faster. - Improved Quality
Continuously monitor and adjust processes in real-time to maintain optimal performance. Digital twins use data analytics to detect inefficiencies, improve product standards, and ensure consistent quality control across production lines. - Sustainability
Reduce waste, energy consumption, and carbon footprint through data-driven optimisation. By simulating production and resource usage, digital twins help companies adopt eco-friendly manufacturing practices and achieve long-term sustainability goals. - Customer Personalisation
Simulate user behaviour to design more tailored products and services. Using insights from digital twin analytics, businesses can enhance the customer experience, improve satisfaction, and create highly personalised solutions that meet evolving market needs.
Future advancements like 6G connectivity will play a key role in enabling faster data transfer, real-time analytics, and ultra-low latency for AI-powered digital twins, unlocking new levels of precision and scalability.
Real-World Applications & Case Studies
1. Manufacturing
Companies like Siemens use digital twins to monitor factory production lines, reducing defects and speeding up output.
2. Healthcare
Philips is developing patient-specific heart models to improve surgical planning and predict treatment outcomes.
3. Energy
GE uses digital twins for wind turbines, forecasting maintenance needs and optimising power output.
4. Smart Cities
Singapore’s Virtual Singapore project creates a 3D city model to manage traffic, plan infrastructure, and improve safety.
5. Aerospace
NASA pioneered digital twins to simulate spacecraft systems and plan maintenance in space.
Challenges and Considerations

While promising, digital twin adoption is not without challenges:
- High initial investment
Setting up a digital twin infrastructure requires IoT sensors, cloud storage, and AI-powered analytics tools, which can be costly for small and mid-sized enterprises. - Data privacy & security concerns
As digital twins rely on real-time data from connected devices, ensuring cybersecurity, data encryption, and regulatory compliance becomes essential to prevent breaches. - Need for skilled professionals
Implementing and maintaining digital twins demands expertise in data science, machine learning, and industrial IoT, which can be difficult to find or expensive to train. - Integration complexity
Connecting legacy systems with modern IoT platforms and cloud-based digital twin software can be challenging, often requiring custom APIs and ongoing maintenance.
As connectivity evolves, 6G networks will play a key role in powering faster, smarter digital twin systems, enabling real-time analytics and ultra-low-latency communication.
How to Implement Digital Twin Technology: Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify Your Goal
Decide whether your primary aim is cost savings, process optimisation, or innovation. Clearly defining your objective helps determine the type of digital twin model, whether it is focused on performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, or product design improvement. - Choose the Right Asset
Start with a high-impact process or machine that can deliver measurable results. It’s best to begin with a system that already generates IoT data, so integration and analysis become easier during your digital transformation journey. - Deploy IoT Sensors
Install IoT sensors to collect real-time operational data such as temperature, vibration, speed, and energy use. These sensors act as the bridge between physical assets and their digital counterparts, ensuring continuous data flow for accurate simulation. - Select a Platform
Choose reliable digital twin platforms like PTC ThingWorx, Siemens MindSphere, or Azure Digital Twins that support AI integration, cloud analytics, and scalable deployment. The right platform enables smooth data visualisation, collaboration, and predictive analytics. - Create the Model
Build your virtual replica using CAD software, 3D simulation tools, or machine learning models. Ensure that your digital twin reflects every operational parameter of the real asset to achieve high simulation accuracy and data consistency. - Test & Optimise
Run multiple what-if scenarios to evaluate system performance under different conditions. Use AI-driven insights to optimise workflows, reduce downtime, and enhance decision-making through data-driven simulations. - Scale Gradually
Once the first model delivers results, expand digital twin implementation to other assets, departments, or even entire production lines. Scaling gradually allows you to fine-tune integrations, control costs, and ensure long-term sustainability.
Example
Siemens uses digital twin technology in its Amberg Electronics Plant in Germany, where every production machine and process has a virtual replica. These digital twins analyse real-time data from IoT sensors to predict equipment failures, optimise manufacturing performance, and reduce defects by over 99%. This integration of AI, cloud computing, and digital simulation has made Siemens a global benchmark for smart factories.
Future Trends: 2025–2030
Expect advancements in:
- AI-powered autonomous twins
Next-generation digital twins will use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to make independent decisions, automatically analyse data, and optimise operations without human input.
These autonomous twins will enable real-time predictive maintenance and smarter industrial automation. - Integration with AR/VR for immersive visualisation
The future will see augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) merging with digital twin platforms to provide immersive 3D visualisations.
Engineers and operators will be able to “step inside” virtual replicas, monitor assets, and make design changes in real time, enhancing training, safety, and collaboration. - Blockchain-secured data sharing
As digital twin ecosystems grow, blockchain technology will ensure secure, transparent, and tamper-proof data sharing across multiple stakeholders. This will be crucial for industries like supply chain, energy, and healthcare, where data integrity and trust are essential. - Self-healing systems that auto-correct performance issues
Emerging self-healing digital twins will automatically detect inefficiencies or equipment failures and auto-correct performance issues in real time. By combining AI, IoT, and predictive analytics, these systems will help businesses achieve near-zero downtime and extend asset lifespan.
Conclusion
Digital twin technology is rapidly transforming industries by connecting the physical and digital worlds. From manufacturing and energy to healthcare and smart cities, its ability to simulate, predict, and optimise systems is driving a new wave of efficiency and innovation.
As the market surges past $100 billion by 2030, businesses that adopt digital twins early will enjoy smarter operations, reduced costs, and sustainable growth. Now is the perfect time to explore this technology and stay ahead in the era of Industry 4.0.
FAQ’s
Is digital twin technology expensive to implement?
Initial setup costs for digital twin technology can be high due to sensors, software, and system integration. However, the long-term benefits, like reduced downtime, improved efficiency, and predictive maintenance, often outweigh the initial investment.
Can small businesses use digital twins?
Yes. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can now adopt digital twins using cloud-based platforms and modular tools that lower costs. This makes the technology more accessible without heavy upfront infrastructure expenses.
Is a digital twin the same as a simulation?
No. While a simulation is a static model based on hypothetical scenarios, a digital twin is a dynamic, real-time virtual model that continuously updates to match the actual physical asset or process it represents.

